MRI Protector Menu(Tap to display menu)
Medical Devices and Hygiene Products
How electromagnetic wave protection works
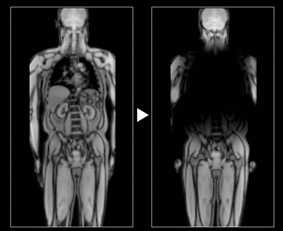
Left: Without MRI protector Right: With MRI protector
The 64MHz and 128MHz RF pulses emitted by MRI heat up metals, which poses a risk to those with metal implants. MRI protectors are made of waterproof nylon material with a high-frequency electromagnetic shielding material called "MG Net" inserted inside. The MRI protector attenuates the RF pulses in the areas it covers by more than 80%, so although imaging is no longer possible, the risk of metal heating is greatly reduced.
In addition, if the set imaging area (FOV) is smaller than the imaging target, the area outside the FOV will be folded back in the phase direction and displayed as an overlapping image. Since MR signals cannot be obtained from the area using the MRI protector, there are no folding back artifacts, and oversampling, phase direction conversion, or presaturation suppression pulse settings are not required. As a result, it is possible to reduce the imaging time.
※ When using an MRI protector, the signal strength may be weakened, resulting in some degradation of image quality.
Aliasing artifacts and the effect of MRI protectors
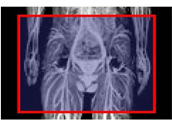
For large FOVs, aliasing artifacts do not appear, so oversampling settings are not required.
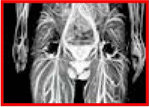
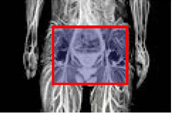
In the case of small FOV, aliasing artifacts will appear, so oversampling etc. settings are required.
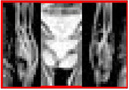
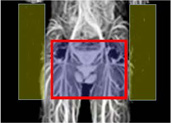
When RF radiation was shielded by using MRI protectors on both arms, aliasing artifacts did not appear even with a small FOV.

MRI Protector Usage Examples
Examples of how MRI protectors can be used are as follows:
Examples of how MRI protectors can be used are as follows:| MRI Protector Type | Examples of use |
|---|---|
| Common to all products |
|
| Neck guard (neck area) | For use with people with non-magnetic metals (cervical stents, metal wires, etc.) embedded in the neck |
| Best Fit Coat (Chest) (Chest to Lower Abdomen) |
|
| Roll Sheet A (Arms and Legs) |
|
| Roll sheet B (partially covers the chest or abdomen) | Used for lower abdominal examinations on patients with tattoos, stents, or sternal wires |
| Mittens (hands and feet) |
|
| Pants (lower abdomen) |
|
Note
Do not use on individuals with implanted devices such as pacemakers or ICDs that are not MRI compatible, as clinical trials have not been conducted.

