MG Work Vest Menu(Tap to display menu)
Various Electromagnetic Protective Clothing
How electromagnetic wave protection works

EMS Padblocks a wide frequency band (0 to several tens of GHz) of static magnetic fields, low-frequency electromagnetic waves, and high-frequency electromagnetic waves. When an AC magnetic field is applied to the loop surface (inside the loop) created by the telemetry coil for communication inside the pacemaker/ICD or the lead wire connecting the device to the heart, a current is induced, causing the pacemaker/ICD to function improperly. Placing two "EMS Pads" on the front and back of the body to cover the loop surface will efficiently block AC magnetic fields.
In addition, even if an AC magnetic field enters the loop surface from the side, it is hardly incident on the loop surface (inside the ring), so the influence of the AC magnetic field from the side is very small. Rather, the influence of the AC magnetic field entering from the front and back due to the magnetic field bending around is greater, so it is optimal to place the "EMS Pad" on the front and back.
■Comparison with other companies' products
MG Work Vest
This facility is designed to protect against electromagnetic waves (alternating magnetic fields and radio waves) generated by equipment and devices within the facility. For details, please see the list of work sites that may affect pacemakers, ICDs, etc. and devices that generate electromagnetic waves.
Other companies
Currently, no other company handles electromagnetic radiation protection clothing for pacemakers, ICDs, etc. We are the only manufacturer in the world of electromagnetic radiation protection clothing for pacemakers, ICDs, etc.
EMS Pad -For MG work vest-
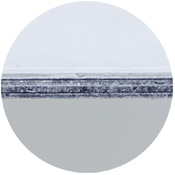
A five-layer EMS pad that provides electromagnetic shielding performance of over 60 dB (99%) at frequencies between 30 kHz and 1 GHz. It has more than twice the surface area of the MG Vest ST for everyday use, and reduces various electromagnetic waves in the workplace. (Insert into the front and back pockets of the vest)

- 1.Low Frequency Magnetic Field
- 2.3 layers of aluminum foil
- 3.Two layers of high permeability magnetic material sheet
- 4.Magnetic field shielding
※Enlarged cross-sectional view
It has a five-layer structure (0.7 mm thick) consisting of three layers of aluminum film and two layers of high permeability magnetic material sheet, and is further enhanced by a PET coating for increased durability.
The combination of a magnetic layer with a maximum magnetic permeability of 200,000 (in a vacuum) and a highly conductive aluminum layer diverts the energy of the low frequency magnetic field. Furthermore, the low frequency magnetic field is attenuated by repeated reflection and absorption.
Comparison of electromagnetic shielding between our products and conventional products (materials)
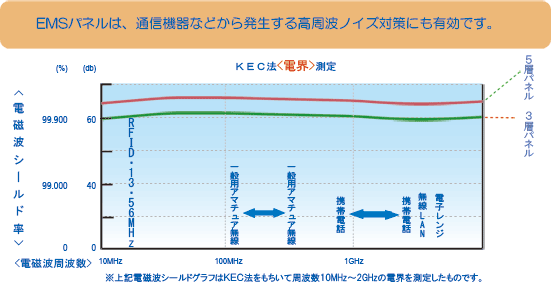
The electromagnetic shielding graph above shows the measurement of the "shielding magnetic field strength" at frequencies from 0Hz to 1000KHz. EMS Pad shields low frequency magnetic fields generated by AC currents and induction cookers, which conventional coating materials have little shielding performance. The graph below shows the electric field shielding data measured by the KEC method at high frequency electromagnetic wave noise.
Theoretical support
1. Theoretical formula for electromagnetic shielding effectiveness
![]()
![]()
The larger S, the greater the electromagnetic shielding effect. Therefore, it is necessary to select a material with a large δ for the electromagnetic shielding material. For the EMS Pad, a high-permeability magnetic material sheet (120 μm thick) was used.

2. Improved electromagnetic shielding rate through multi-layering of materials
The theoretical formula for the electromagnetic shielding effect S when the material is multi-layered is shown below.

The larger S is, the higher the electromagnetic shielding effect is. Electromagnetic shielding performance is improved by laminating electromagnetic shielding materials. The EMS Pad is made up of a five-layer structure of aluminum foil and high-permeability magnetic material sheets.
3. Shielding magnetic field strength measurement test
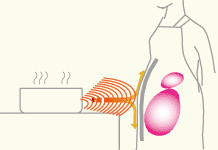
The shielding magnetic field strength is measured using the following method [Figure 2]. A tracking pulse is transmitted from a transmitting loop antenna and received by a receiving loop antenna separated by the material under test, and the shielding strength is measured.

▲ Figure 2 Shielding magnetic field strength measurement test method
The results of the Shielding magnetic field strength measurement test of the EMS Pad are shown in Figure 3. This sheet is made up of a five-layer structure of aluminum foil and high-permeability magnetic material sheets, and despite its thickness of 0.7 mm, a shielding magnetic field strength measurement test at the material value confirmed a maximum shielding rate of approximately 60 dB (99.9%) in low-frequency electromagnetic fields from 100 Hz to 300 kHz. It has been confirmed that the low-frequency electromagnetic field emitted by induction cookers has the strongest energy in the 20 kHz to 30 kHz range, and the shielding rate in that vicinity was confirmed to be 60 dB (99.9%).

▲Figure 3. Shielding performance measurement data
(※Note: This is a logarithmic scale of 10 squared, so it is not uniform.)
References: Latest Electromagnetic Wave Absorption and Shielding, Nikkei Technical Books



