MG Vest VIP Menu(Tap to display menu)
Various Electromagnetic Protective Clothing
EMS Pad
Five-layer EMS pad (insert into your inner clothing pocket) that attenuates low-frequency magnetic fields from 30kHz to 300kHz by 45 to 60dB (99.35 to 99.99%). *Made of lightweight, soft material.

- 1.Low Frequency Magnetic Field
- 2.3 layers of aluminum foil
- 3.High permeability magnetic material sheet, 2 layers
- 4.Magnetic field shielding

※Enlarged cross-sectional view
Five-layer structure (thickness 0.7 mm) consisting of three layers of aluminum film and two layers of high-permeability magnetic material sheets
The combination of a magnetic layer with a maximum magnetic permeability of 200,000 (in a vacuum) and a highly conductive aluminum layer diverts the energy of low-frequency magnetic fields. Furthermore, the low-frequency magnetic fields are attenuated by repeatedly reflecting and absorbing them.
Comparison of electromagnetic shielding between our products and conventional products (materials)
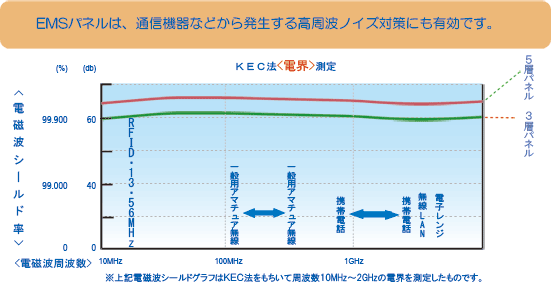
The electromagnetic wave shielding graph above shows the measurement of "shielding magnetic field strength" at frequencies from 0Hz to 1000KHz. EMS pads shield low-frequency magnetic fields generated by AC currents and induction cookers, which conventional coating materials have little shielding ability. The graph below shows electric field shielding data measured by the KEC method for high-frequency electromagnetic wave noise.
Theoretical support
1.Theoretical formula for electromagnetic shielding effectiveness
![]()
![]()
The larger S, the greater the electromagnetic shielding effect. Therefore, it is necessary to select a material with a large δ for the electromagnetic shielding material. For the EMS pad, a high-permeability magnetic material sheet (120 μm thick) was used.

2. Improved electromagnetic shielding rate through multi-layering of materials
The theoretical formula for the electromagnetic shielding effect S when the material is multi-layered is shown below.

The larger S is, the higher the electromagnetic shielding effect is. Electromagnetic shielding performance is improved by laminating electromagnetic shielding materials. The EMS pad is made up of a five-layer structure of aluminum foil and high-permeability magnetic material sheets.
3. Shielding magnetic field strength measurement test
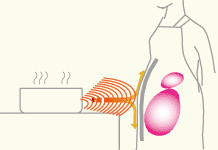
The shielding magnetic field strength is measured using the following method [Figure 2]. A tracking pulse is transmitted from a transmitting loop antenna and received by a receiving loop antenna separated by the material under test, and the shielding strength is measured.

▲Figure 2. Shielding magnetic field strength measurement test method
The results of the shielding magnetic field strength measurement test for the EMS pad are shown in Figure 3. This sheet is made up of a five-layer structure of aluminum foil and high-permeability magnetic material sheets, and despite its thickness of 0.7 mm, a shielding magnetic field strength measurement test at the material value confirmed a maximum shielding rate of approximately 60 dB (99.9%) in low-frequency electromagnetic fields from 100 Hz to 300 kHz. It has been confirmed that the low-frequency electromagnetic field emitted by induction cookers has the strongest energy in the 20 kHz to 30 kHz range, and the shielding rate in this vicinity was confirmed to be 60 dB (99.9%).

▲Figure 3. Shielding performance measurement data
(※Note: This is a logarithmic scale of 10 squared, so it is not uniform.)
References: Latest Electromagnetic Wave Absorption and Shielding, Nikkei Technical Books



